- Mar 12, 2024
- Internet Of Things
- 9262
Share this post on:

Today, we live in an era of digital money, and the Internet of Things (IoT) is playing a crucial role in these advancements. The integration of IoT solutions with banking and finance has led to more intuitive and innovative ways to manage funds for business owners.
In FinTech, IoT offers several benefits, such as improving efficiency, security, and customer experience. The blend of the Internet of Things (IoT) and FinTech has brought new possibilities and has become increasingly important in the finance industry. Both technologies are transforming our daily lives and changing how businesses work and manage money.
From connected car platforms with built-in insurance billing to predictive maintenance solutions, the applications of IoT in FinTech are endless.
Benefits of IoT in FinTech
Over recent years, the Internet of Things (IoT) technology is being used by banks for various purposes that involve everything from market research to risk assessment. Incorporating IoT technologies into banking and finance helps increase efficiency, improve communication, and strengthen relationships with customers.
Some key advantages of integrating IoT into fintech include:
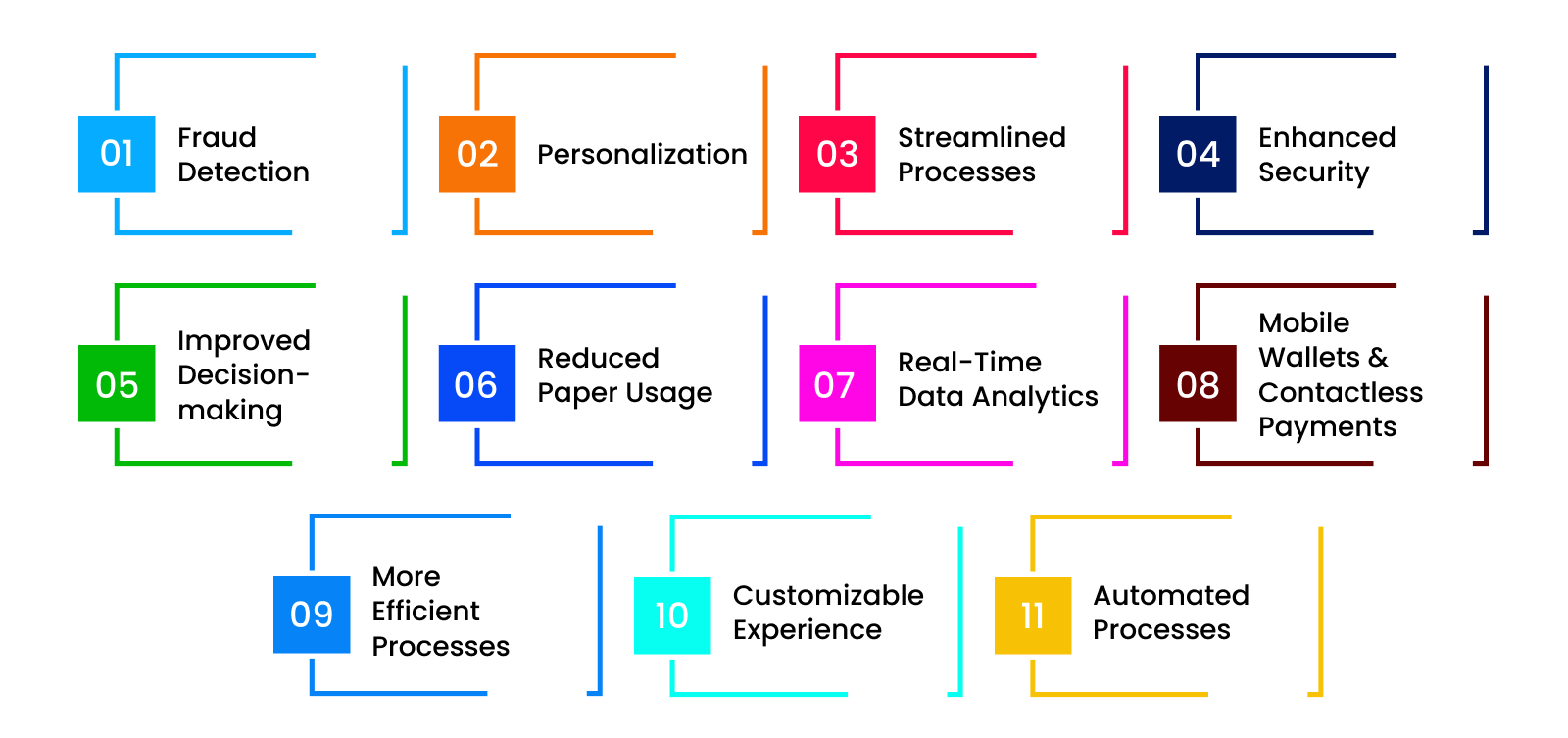
- Fraud detection: IoT technology has given financial institutions access to more data than ever before, which helps improve fraud detection. This technology includes sensors to track unusual behavior, such as high transaction volumes outside business hours, unrecognized IP addresses, and changes in patterns from regular customers.
Moreover, financial institutions can prevent significant losses and protect their clients’ assets by detecting potential issues quickly.
- Personalization: Financial services often depend on personal touches, from greeting customers by name at the bank branch to providing custom recommendations for investments. IoT enables banks to create stronger connections with consumers by providing them with tailored experiences based on past activity and preferences.
For instance, wearable devices can alert people if they overspend their budget or forget to make recurring payments. Additionally, smart home gadgets allow users to control everything related to finances within their home ecosystems.
- Streamlined processes: Financial institutions can simplify operations and boost productivity using IoT technologies such as biometric authentication, automation, machine learning, natural language processing, artificial intelligence, and robotics process automation.
These systems save employees time by streamlining tasks, reducing errors, cutting costs, and allowing customers to accomplish more self-service activities without assistance. This technology creates a better user experience, resulting in higher levels of satisfaction and loyalty.
- Enhanced security: IoT empowers banks and other financial organizations with additional layers of safety. Devices such as sensors can monitor cash machines 24/7, alerting authorities immediately upon detecting anything serious, while cameras keep watch over suspicious behavior around buildings.
Furthermore, connected devices like credit cards embedded with chips can reduce payment disputes and fraudulent charges, giving customers a sense of safety and trust.
- Improved decision-making: Collecting and analyzing vast amounts of data allows institutions to gain insights into consumer behavior. It empowers businesses to make smarter decisions regarding products and service offerings.
Banks and credit card providers may choose to leverage this knowledge to promote targeted promotions designed to appeal to individual needs. Also, managers might use IoT data to refine investment strategies and generate higher returns for their clients.
- Reduced paper usage: Going digital reduces environmental impact and saves money on printing expenses associated with maintaining records and producing financial documents manually. Aside from operational cost savings and improved sustainability, online account management tools provide customers with convenient access to information whenever required.
- Mobile wallets and contactless payments: Wearable tech and mobile phones enable faster checkout times for purchases at physical stores. IoT makes the transition to cashless societies easier and more efficient. These benefits retailers and shoppers who no longer need to carry cash or plastic cards around with them.
Removing those traditional methods limits theft situations. Smart cards issued by financial institutions contain encrypted codes to ensure protection against unauthorized use. It saves sensitive personal details from becoming compromised during monetary exchanges.
- More Efficient Processes: One of the main advantages of incorporating IoT into fintech is its potential for increased efficiency. IoT devices monitor and track every aspect of a person's financial journey. It manages everything from loan repayments to stock market trades, saves countless hours, and reduces the risk of human error.
Additionally, IoT analytics allow companies to identify areas for improvement in back-end operations. It frees up resources, optimizes supply chain logistics, and minimizes downtime. By leveraging advanced sensor technologies and cloud computing capabilities, fintech providers can automate internal processes, streamline customer interactions, and increase revenue.
- Real-Time Data Analytics: Another main benefit of using IoT in fintech is real-time data analytics. IoT sensors capture massive amounts of data, financial service providers now have access to valuable information. They can analyze customer spending patterns, identify high-risk behaviors, and create personalized models for predicting future outcomes.
IoT data analysis helps institutions to understand their customers' needs better. This help businesses tailor products and services accordingly, maximizing the lifetime value of each client. Also, by utilizing data visualization techniques, users can gain valuable insights from complex datasets, and make informed decisions more confidently.
- Customizable Experience: Banks and financial companies can gather large quantities of data on customer habits and spending patterns using IoT services. This insight allows them to produce highly individualized products and services that fit an individual's specific requirements, helping build brand loyalty.
Additionally, IoT facilitates real-time monitoring of client accounts. A perfect example of this includes using wearables and other IoT devices in combination with apps and websites for personal banking. Using wearables, customers get up-to-date advice throughout the day about their finances, including transaction summaries and budget progress reports. By doing this, they can achieve greater awareness of their funds and take proactive steps to enhance their fiscal standing.
- Automated Processes: By deploying IoT gadgets, the financial industry can automate many regular manual jobs, which lessens the probability of human error and increases productivity.
Furthermore, these changes permit staff members to spend more time focusing on critical high-value tasks, raising their worth to the enterprise. Examples include automatic bill settlements for utilities, mortgage repayments, subscriptions, and employee salaries.
What are the applications of IoT in Banking and Financial Services?
Technology continues to shape every aspect of our daily lives. With that, the field of banking and financial services has seen significant changes over the past decade due to technological innovation. One such innovation is the Internet of Things (IoT), which refers to the interconnected network of physical objects that have embedded sensors and processors.
Here we explore some of the applications of IoT in the banking and financial services sector.
 Cash App: Cash App is a popular mobile application that allows users to make instant transactions using their smartphones. In March 2021, Cash App reached a valuation of $54 billion, making it one of the fastest-growing startups in history.
Cash App: Cash App is a popular mobile application that allows users to make instant transactions using their smartphones. In March 2021, Cash App reached a valuation of $54 billion, making it one of the fastest-growing startups in history.
Cash App offers several features, including easy fund transfers between individuals without any fees, direct deposit of paychecks, and the ability to purchase digital assets such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies. The app also offers virtual Visa card functionality, allowing users to link their accounts to merchants accepting debit/credit cards.
Additionally, users can earn rewards points by referring friends and family members to join Cash App.
Mastercard: Mastercard offers branded credit and debit cards. Launched in 1966 as a joint venture between several large American banks, Mastercard now encompasses over 24,000 member financial institutions located worldwide. Its core competencies involve processing electronic payments via point-of-sale machines, ATM withdrawals, internet purchases, phone orders, and eCommerce transactions.
In addition to issuing payment cards, Mastercard engages in other business segments:
- Network Solutions: Providing transaction authorization services, fraud detection, and secure functions connecting buyers, sellers, and financial institutions globally. They maintain vast infrastructure, ensuring data and transactions are involved properly.
- Advertising and Marketing Services: Helping clients grow customer bases by leveraging Mastercard's huge network reach. Their loyalty program encourages customers to participate in charitable initiatives while promoting the brand.
- Digital Payments: Through partnerships like Vocalink, Mastercard helps develop faster payment schemes facilitating near real-time transferring of funds between countries. The company launched Mastercard Send service, enabling easy, efficient person-to-person money remittances domestically and internationally.
- New Commercial Models: Exploring innovative ways of expanding financial inclusion utilizing technologies like QR codes and biometric identification, reaching underserved communities lacking conventional bank account access. Mastercard Labs focuses on research and development to create great products and services tailored to emerging markets specific needs.
Metromile: Metromile Inc. is a US-based technology startup providing pay-per-mile car insurance and telematics services. They offer services based on individual driving habits that aim at reducing auto insurance premiums.
Metromile offers an innovative approach that uses data analytics, machine learning algorithms, and IoT connectivity to offer policyholders customized coverage plans.
Top challenges of IoT in FinTech
The landscape of banking and finance is undergoing various changes in recent years. With new regulations, changing market conditions, emerging technologies, and increasing competition, today's industry faces numerous challenges.
Let us dive deeper into the top ten challenges faced by modern banking and finance firms:
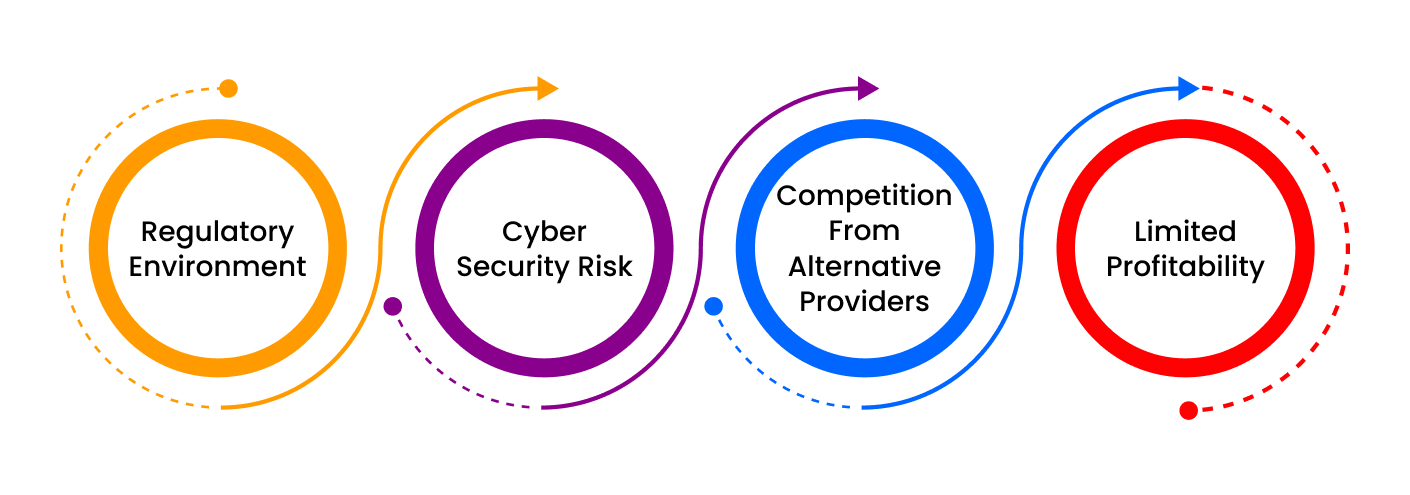
- Regulatory environment: The laws and regulations designed to safeguard customers’ interests often limit business flexibility, increase operating costs, and impede growth. Staying ahead of changing policies, navigating complex compliance frameworks, and ensuring adherence pose substantial obstacles to many institutions.
- Cybersecurity risk: With the increasing demand for connected networks, cloud computing, mobile devices, and online banking platforms has increased the threats of cyber-attacks, hackers, and data breaches.
Businesses can mitigate threats by investing in advanced security measures and protocols, including firewalls, encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular audits. Failure to maintain robust defenses can lead to costly consequences, including reputation damage.
Ensuring safe systems requires significant investment in advanced firewalls, antivirus software, multi-factor authentication protocols, encryption, patch management, and regular security audits to counter sophisticated cybercriminals attempting large-scale attacks or launching targeted phishing campaigns.
- Competition from alternative providers: Non-bank players like tech giants Apple, Amazon, Alibaba, Tencent, PayPal, Square, and others threaten traditional banking models by offering streamlined financial products, mobile apps, and seamless user experiences. Businesses must adopt innovative approaches to stay relevant that meet evolving customer demands efficiently, effectively, and economically.
- Limited profitability: Intense competition generates additional income without compromising service quality or customer satisfaction. Expanding fee structures, diverse product lines, launching cross-selling campaigns, creating new partnerships, and implementing leaner operating models may mitigate margin pressures but require careful planning and execution.
Conclusion:
IoT plays a vital role in bringing innovation and improvement to fintech industries. From creating a positive UX to simplifying procedures and cutting overhead costs, the interconnection of various devices with IoT provides endless possibilities across all verticals of FinTech. Even though there are many risks involved, the advantages significantly outweigh the disadvantages.